Treatment at Derma Solution
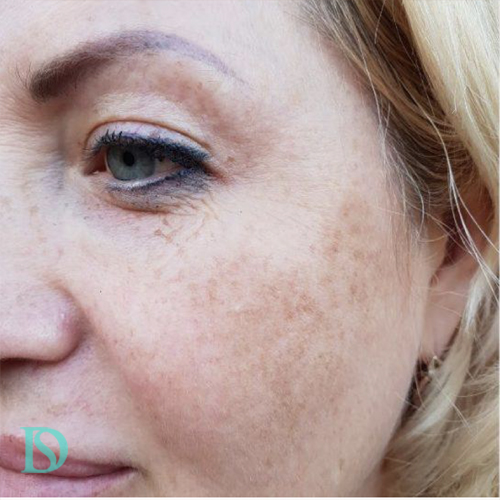
Pigmentation Course

Pigmentation issues can be caused by several factors, including:
- Lack of Water: Dehydrated skin can become uneven in tone and more susceptible to pigmentation problems such as dullness and dark spots.
- Sensitivity: Sensitive skin can react more severely to environmental stressors, leading to uneven pigmentation and exacerbating existing issues.
- Inflammation: Skin inflammation from conditions like acne or eczema can result in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, where dark spots form after the inflammation subsides.
- Sun Exposure: UV rays stimulate excessive melanin production, leading to sunspots and hyperpigmentation.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations in hormones can cause conditions like melasma, resulting in uneven pigmentation and dark patches on the skin.
Treating pigmentation issues involves a variety of methods, each targeting different types of hyperpigmentation, such as melasma, age spots, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Here are some of the most effective treatments:
1. Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone: A widely used skin-lightening agent that reduces the production of melanin. It’s often prescribed for melasma and age spots.
- Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives like tretinoin that promote cell turnover, helping to fade dark spots and improve skin texture.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that brightens the skin and inhibits melanin production, reducing pigmentation over time.
- Azelaic Acid: Helps to treat hyperpigmentation and acne simultaneously by reducing melanin production and calming inflammation.
- Niacinamide: A form of Vitamin B3 that reduces the transfer of melanin to skin cells, helping to lighten dark spots.
2. Chemical Peels
- Glycolic Acid Peels: Use alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) to exfoliate the skin, promoting the shedding of pigmented cells and revealing brighter skin underneath.
- Salicylic Acid Peels: Particularly effective for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, especially in acne-prone skin.
- TCA Peels: Trichloroacetic acid peels are stronger and can treat deeper pigmentation issues, though they require longer recovery time.
3. Laser Treatments
- Fractional Laser Resurfacing: Targets pigmentation by creating micro-injuries in the skin, promoting new collagen growth and breaking down excess melanin.
- Q-Switched Laser: Specifically targets melanin in the skin, breaking it down without damaging surrounding tissue, making it ideal for treating age spots and sun damage.
- IPL (Intense Pulsed Light): Uses broad-spectrum light to target and break down pigmentation, improving overall skin tone and texture.
4. Microdermabrasion
- Crystal or Diamond Microdermabrasion: Exfoliates the upper layer of the skin to remove pigmented cells. This is a milder option compared to chemical peels and is suitable for minor pigmentation issues.
5. Microneedling
- Collagen Induction Therapy: Involves using tiny needles to create micro-injuries in the skin, stimulating collagen production and helping to disperse uneven pigmentation.
6. Natural Remedies
- Licorice Extract: Contains glabridin, which helps inhibit melanin production.
- Aloe Vera: Contains aloesin, which can help reduce pigmentation and soothe the skin.
- Kojic Acid: Derived from fungi, it inhibits melanin production and can help lighten dark spots.
7. Sun Protection
- Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Regular use of sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher is crucial in preventing pigmentation from worsening. UV exposure is a significant trigger for hyperpigmentation, so protection is key.
Combination Treatments
Often we recommend a combination of these treatments for optimal results. For instance, RF Micro Needling alongside a series of chemical peels or laser sessions can enhance the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
Consultation
It’s important to consult a professional to determine the most appropriate treatment based on your specific type of pigmentation, skin type, and overall skin health. This ensures the safest and most effective approach to achieving clearer, more even-toned skin.
We at Derma Solution will alway conduct an AI based advanced skin analysis to be able to offer the best solution. Also, it’s a great tool to use when comparing before and after photos.
Pigmentation refers to the coloring of the skin, which is primarily determined by melanin, a pigment produced by melanocytes. Various types of pigmentation issues can occur when there is either an excess or a deficiency of melanin. Here are the main types of pigmentation:
1. Hyperpigmentation
- Melasma:
- Description: Melasma is characterized by dark, discolored patches on the skin, typically on the face. It is often triggered by hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or with the use of birth control pills.
- Appearance: Brown or gray-brown patches, usually symmetrical and most commonly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip.
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH):
- Description: PIH occurs after an injury or inflammation of the skin, such as acne, eczema, or a cut. It results from the skin’s response to inflammation, leading to increased melanin production in the affected area.
- Appearance: Darker spots or patches where the skin was injured or inflamed.
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines):
- Description: Sunspots, also known as liver spots or age spots, are flat, brown spots that develop on sun-exposed areas of the skin over time, typically due to prolonged UV exposure.
- Appearance: Small, dark patches, most commonly found on the face, hands, shoulders, and arms.
- Freckles (Ephelides):
- Description: Freckles are small, flat, brown spots that are more common in people with fair skin and are caused by sun exposure and genetic factors.
- Appearance: Small, round, and light to dark brown in color, usually appearing on sun-exposed areas like the face, neck, and arms.
- Hyperpigmentation Due to Medication:
- Description: Some medications can cause increased pigmentation as a side effect, such as certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and antimalarials.
- Appearance: Diffuse or localized darkening of the skin, depending on the medication and the area affected.
2. Hypopigmentation
- Vitiligo:
- Description: Vitiligo is a condition where the skin loses its pigment cells (melanocytes), leading to white patches of skin. It can affect any part of the body, including the hair and inside of the mouth.
- Appearance: Irregular, depigmented white patches of skin, often symmetrical and progressive.
- Albinism:
- Description: Albinism is a genetic condition characterized by a complete or partial lack of melanin, leading to very light skin, hair, and eyes. Individuals with albinism are more susceptible to sunburn and skin cancers.
- Appearance: Extremely pale skin, white or light-colored hair, and light-colored eyes.
- Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation:
- Description: This occurs when a skin injury or inflammation leads to a loss of pigment in the affected area, often after conditions like psoriasis, eczema, or burns.
- Appearance: Lighter patches of skin where the injury or inflammation occurred.
3. Other Forms of Pigmentation
- Nevus (Moles):
- Description: Moles are common benign growths on the skin that occur when melanocytes grow in clusters rather than being spread evenly throughout the skin. Most moles are harmless, but they can sometimes become cancerous.
- Appearance: Usually brown or black, they can be flat or raised and vary in size and shape.
- Café-au-Lait Spots:
- Description: These are light brown skin patches that can be present at birth or develop in early childhood. They are usually benign but can be associated with certain genetic conditions like neurofibromatosis.
- Appearance: Flat, light brown patches that vary in size, usually oval-shaped.
- Mongolian Spots:
- Description: These are blue or grayish patches that appear on the skin, usually in infants of Asian, African, or Native American descent. They are caused by the presence of melanocytes deep in the skin.
- Appearance: Blue-gray spots, typically on the lower back or buttocks, often fading with age.
Understanding the type of pigmentation is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment or management approach. If you’re experiencing unusual changes in your skin’s pigmentation, it’s important to consult a dermatologist for accurate diagnosis and treatment options.
Treatment Area
- Face
- Nose
- Cheeks
- Neck
- Hands
- Upper body
- Lower body
Procedure Time:
15 – 30 mins
Back to Work:
Next day
Anaesthetic:
According to your needs
Full Recovery:
24 hours
Sensitivity Period:
24 hours
Duration of results:
Immediately
Book Now:
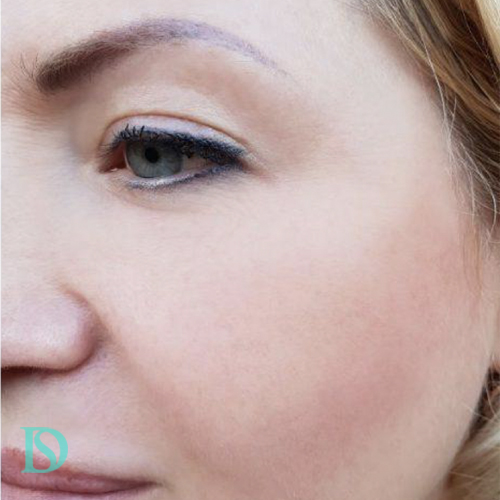

Price GuaranteeOn All Treatment
Derma Solution offers a price guarantee on all of our treatment ranges. If you are able to find a treatment that we offer cheaper anywhere in Copenhagen we will match the price.
Pigmentation Course
Treatment Prices
-
Full Face Personalised
-
Neck Personalised
-
Chest Personalised
-
Neck + Chest Personalised
-
Hands Personalised
-
Single body part (e.g. forehead, Cheeks, Nose) Personalised
-
Consultation DKK 0.00
Pigmentation Course
Frequently Asked Questions
We can safely treat any benign hyperpigmentation, including freckles, sun spots, age spots and café au lait birthmarks.
Any area of the body can be treated safely and effectively. Our most common treatment areas include face, neck, chest, arms and hands.
Your treatment plan will depend on many factors such as the location, depth, size and type of pigmentation. Some lesions will require several treatments for optimal results, where some can be resolved in a single treatment. On average, patients will need 2-3 sessions for complete removal. Subsequent treatments can be scheduled for four weeks after your treatment.
The frequency of your pigmentation removal appointments will be based on clinical judgment. For most patients, treatment will be performed every 4 – 8 weeks.
Pigmented lesions that have been removed will not return after your laser treatments. However, various factors such as aging, changes in hormone levels or UV exposure can stimulate new hyperpigmentation. Laser pigmentation removal treatments do not prevent new hyperpigmentation from occurring.


